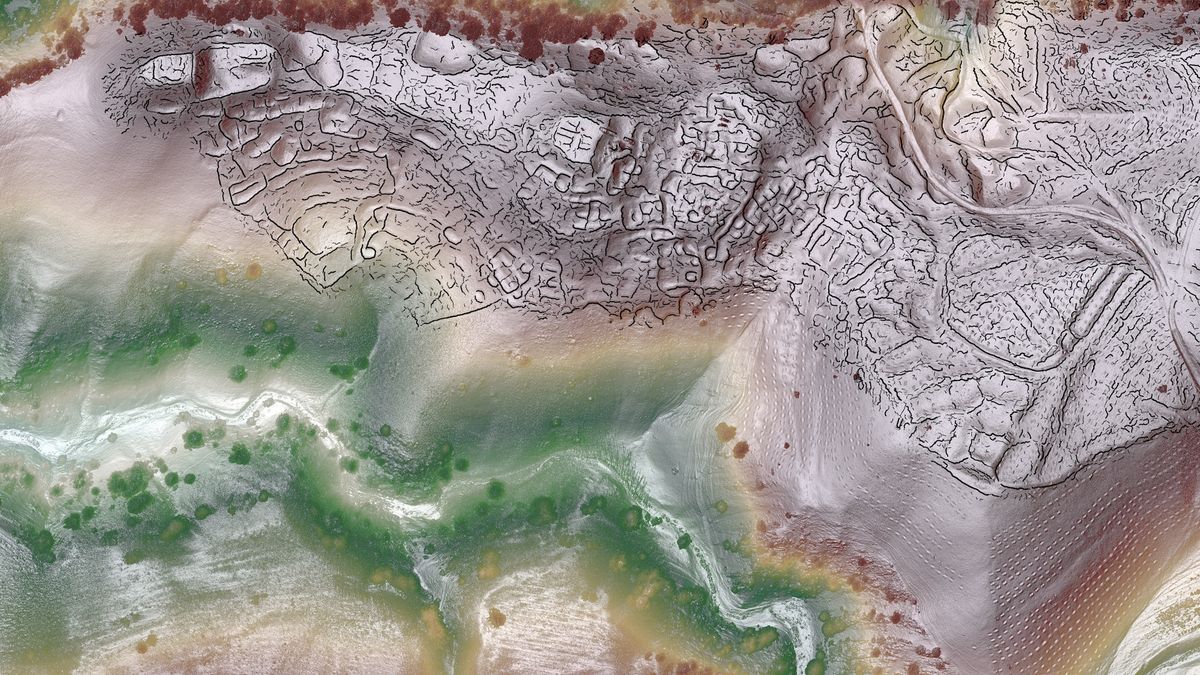
A large crater in Siberia dubbed the “gateway to the underworld” by locals is continuous to develop bigger, new drone footage reveals.
The footage, which was launched on July 12, provides viewers a chicken’s-eye view of the Batagay (additionally spelled Bagatayka and Batagaika) crater, thought-about to be the most important permafrost melancholy on this planet, in response to Ruptly.television.
Protecting roughly 0.3 sq. miles (0.8 sq. kilometers) — equal to the world of about 145 soccer fields — the deep scar reducing by way of the east Siberian woodlands was possible triggered by deforestation through the Forties. This led to erosion, which then exacerbated seasonal melting of the permafrost and created a “megaslump,” or the large crater within the floor. As a result of the permafrost on this area is comprised of 80% ice, the big quantities of melting pressured sediment on the hillside to break down, revealing what appears like a large gash slashing by way of the panorama in Russia’s Sakha Republic.
Associated: Zapotec ‘entrance to the underworld’ found underneath Catholic church in Mexico
And it isn’t simply drone imagery that reveals that the crater continues to develop. Over time, satellite tv for pc imagery has additionally confirmed that the megaslump has grown in dimension. Because the land has retreated, it has revealed “tens of hundreds of years of frozen stays,” courting way back to the Center Pleistocene, which ended 126,000 years in the past.
In a single examine, the soften allowed scientists to entry bison meat that had been frozen for roughly 8,000 years, giving researchers new perception into animals and vegetation that when inhabited the area.
Scientists aren’t positive precisely how rapidly the crater is increasing. Nonetheless, locals declare that within the final a number of years, it has grown between 66 toes and 98 toes (20 and 30 m) at sure factors, in response to NDTV, a TV station in New Delhi.
“That is one thing very uncommon,” Alexey Lupachev, a senior researcher on the Institute of Physicochemical and Organic Issues of Soil Science on the Russian Academy of Sciences, advised Ruptly.television. “It is a distinctive object of nature, which permits us to see the historical past of Earth over a interval of half 1,000,000 years preserved in permafrost.”

















.jpg)



